Types of synoptic situations that favored the arrival of sargasse to the cuban coasts in the period july 2021 - june 2023
Main Article Content
Abstract
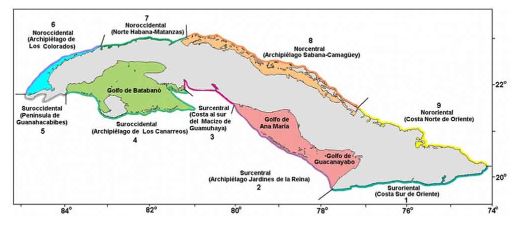
In Cuba, both on the northern and southern coasts, the presence of sargassum has occurred and has been reported from various observation angles by different authors. These macroalgae cause an increase in the mortality of several marine species such as fish, sea turtles and coastal invertebrates and can have a severe impact on local fishing, aquaculture and tourism. For this reason, it is of great importance to know the favorable atmospheric conditions for the movement of sargassum. Taking into account the above, the main objective is to analyze the Types of Synoptic Situations favorable for the arrival of sargassum to the Cuban coasts. In this article, the classification of the Types of Synoptic Situations developed by Lapinel in 1988 was used. It was demonstrated that the synoptic situation that most frequently influences the Cuban archipelago is the migratory continental anticyclone, followed by the subtropical oceanic anticyclone and the extended anticyclonic flow. In addition, it was shown that the winds of the first and second quadrant, imposed by high pressure systems, are important factors in the arrival of sargassum to the Cuban coastlines. On the other hand, it was found that the southern coast of Cuba is more affected by the arrival of sargassum than the northern coast, with the eastern region being the one that presented a greater number of reports of the arrival of these macroalgae, mainly the Guantánamo province. Also, it was evident that in the rainy period (May - October) the Cuban coasts are most affected by the arrival of sargassum, with the months June and September being the most representative.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Those authors who have publications with this journal accept the following terms of the License Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0):
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
- Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
- No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
The journal is not responsible for the opinions and concepts expressed in the works, they are the sole responsibility of the authors. The Editor, with the assistance of the Editorial Committee, reserves the right to suggest or request advisable or necessary modifications. They are accepted to publish original scientific papers, research results of interest that have not been published or sent to another journal for the same purpose.
The mention of trademarks of equipment, instruments or specific materials is for identification purposes, and there is no promotional commitment in relation to them, neither by the authors nor by the publisher.
References
Bamba, A., Abraham, S., Fontaine, A., Fardin, F., Franks, J. (2013). Paper on the Sargassum seaweed invasion of West African and Caribbean coasts. UNEA-2 Side Event.
Caballero, J.A., Acosta, G., Hernández, C. (2020). El sargazo, un fenómeno complejo. Ciencia. Revista de la Academia mexicana de Ciencias. Vol.71 Num.4.
Cuesta, O., Toledo, H., Vidaillet, J. (1995). Características del NO2 y los Tipos de Situaciones Sinópticas en 2 localidades de la ciudad de La Habana. Rev Cubana Hig Epidemiol. V.33 n.1 La Habana. Ene-jun. 1995.
Frazier, J.T., T.L., Linton, R.K., Webster. (2014). Advanced prediction of the Intra-Americas Sargassum season through analysis of the Sargassum Loops System using remote sensing technology. Journal of the American Shore and Beach Preservation Association. 83(4): 15-21.
García, E.A., López, R., (2019). Comportamiento de las tss y las variables meteorológicas en el periodo 2015 – 2017.
Gómez, R., Zúñiga, D., Pazos, C., González, M., (1994). Influencia de algunas variables hidrometeorológicas en los arribazones de Sargassum sp. en Playa Larga, Cayo Coco. Memorias del III Congreso de Ciencias del Mar, La Habana, p. 625.
González, P., (1995). Caracterización de las especies de Sargassum de Playa Gibara, Cuba. Tesis de Diploma, Universidad de Oriente, 80 pp.
Guzmán, A. (2019). Análisis espacio – temporal de la distribución del sargazo (Sargassum natans y S. fluitans) en la costa de Quintana Roo, México. Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana.
Hill, B. (2016). An Analysis of the Factors That Influence the Sargassum Migratory Loop. Texas A&M University. Tesis de Maestría, 30 pp.
Lapinel, B. (1988). La circulación atmosférica y las características espacio – temporales de las lluvias en Cuba. Tesis presentada en opción al grado científico de candidato a Doctor en Ciencias Geográficas. INSMET. La Habana. Cuba.
Maurer, S.A., Neef, D.E., Stapleton, S. (2015). Sargassum accumulation may spell trouble for nesting sea turtles. Eco. Soc. Ame., pp. 394.
Mitrani, I. (2017). Meteorología marina. La Habana, Cuba: Citmatel.
Moreira, L., Cabrera, R., Suarez, A.M. (2006). Evaluación de la biomasa de macroalgas marinas del género Sargassum C. Agardh. (Phaeophyta, Fucales). Rev. Invest. Mar., 27(2):115-120.
Moreira, A., Alfonso, G., (2013). Inusual arribazón de Sargassum fluitans (Børgesen) en la costa centro-sur de Cuba. Rev. Invest. Mar., 33(2).
Piña, J.J., Balbín, A.I., Pérez-Cordovés, I.A., (2010). La contaminación por metales pesados en sargazos procedentes de la costa sur en la península de Guanahacabibes, ¿aún no es preocupante? Revista Cubana de Química, XXII(1): 83-88. http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=443543719011.
Soler, E., Lecha, L., Sanchez, L., Verdecia, Y., (2020). Catálogo de los Tipos de Situaciones Sinópticas que influyen sobre Cuba. ResearchGate. November 2020. DOI: http://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.122542.20802.
Torres-Conde, E.D., Martínez-Daranas, B., (2019). Lista de especies de las arribazones de macrofitobentos en cinco playas de Habana del Este, Cuba. Revista de Investigaciones Marinas, 39(1): 39-49.
Zúñiga, D., (1996). Evaluación del Sargassum de arribazón en las costas de Cayo Coco y la influencia de las variables meteorológicas. Tesis de Maestría, Centro de Investigaciones Marinas, Universidad de La Habana, 78 pp.
Vinagre, F., Zamacona, A., & Casseb, T. (2019). Sargassum: Another Bump in Tourism. Credit Suisse: Mexico City, Mexico, 12 pp.
Wang, M., Hu, Ch., Barnes, B.B., Mitchum, G., Lapointe, B., Montoya, J.P. (2019). “The great Atlantic Sargassum belt”, Science, 365:83-87. Disponible en: http://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw7912.
Webster, R., Linton, T. (2013). Development and Implementation of Sargassum Early Advisory System (SEAS). Shore & Beach, 81: 1-6.